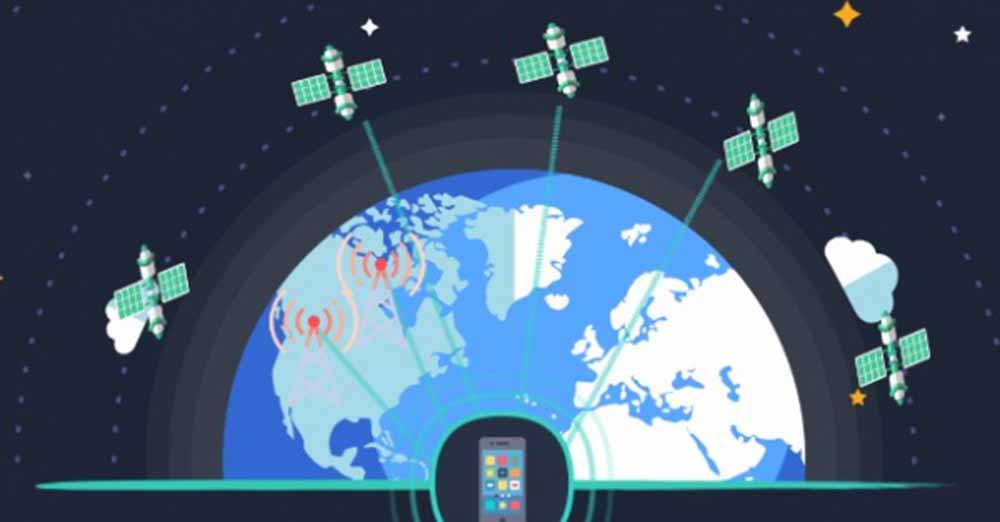
Satellite phone potential The road to satellite phone ubiquity has not been smooth. SpaceX, which has established a satellite communication network, and T-Mobile, which has established a mobile phone communication network, have agreed to work together to enable mobile phone access to the satellite communication network.
Apple has also agreed to work with GlobalStar, which established a satellite communication network. As September neared last week, speculation that the iPhone 13 would come with satellite communications was wrong. Now, when the iPhone 14 comes out on September 7, it is speculated that it will come with satellite communication. New business AST SpaceMobile also plans to launch satellite phone service next year and has partnered with Vodafone, which has established a mobile phone network.

What makes connecting phones to satellites so difficult? Difficulty with range and power. Generally, mobile phones are designed to talk to cell towers within 10 kilometers (6 miles). The satellites are at a distance of 500 km from the earth. They are orbiting the Earth at a speed of 17,000 miles per hour. SpaceX’s Internet satellite network uses a 20-inch by 12-inch satellite on the ground.
To produce a smartphone with a large size, like a sling, that can be placed in a shirt pocket. Impossible to use. So, since the phone is weak, the satellite needs to be powerful. We need to be able to capture very weak signals. In other words, you need to use a large antenna on the satellite to directly connect the phone to the satellite.

To install a large antenna, the satellite must be large. Starlink’s second-generation satellite with a large antenna is so large that it can only be carried by Starship and sent into Earth’s orbit. At present, it is impossible to deliver with interplanetary launch rocket systems. When the Starship goes up and down regularly, it will carry and deliver the second generation satellites again and again.
When it is finished, there will be enough second generation satellites in the earth’s orbit, and it will be convenient to communicate directly with the phone. Another challenge is obtaining the electromagnetic spectrum, which includes the radio frequencies used by phones and satellites to transmit to each other for communications. For example, SpaceX has allowed SpaceX to use some of the radio frequencies it has licensed from mobile operator T-Mobile to connect phones and spacecraft.

Apple has purchased 11 new satellites from satellite operator GlobalStar for $300 million for Apple’s satellite phone program. We hope to find out at Apple’s “Far Out” event on September 7th just how far the satellite phone can go. One advantage is that Globalstar has acquired the license to use the radio frequency spectrum not only in the United States but also around the world, so iPhone satellite communication can also be used in countries licensed by Globalstar.